[ZYNQ] 启动流程
https://github.com/carloscn/blog/issues/147
[Embedded] ZYNQ-UltraScale+的启动流程
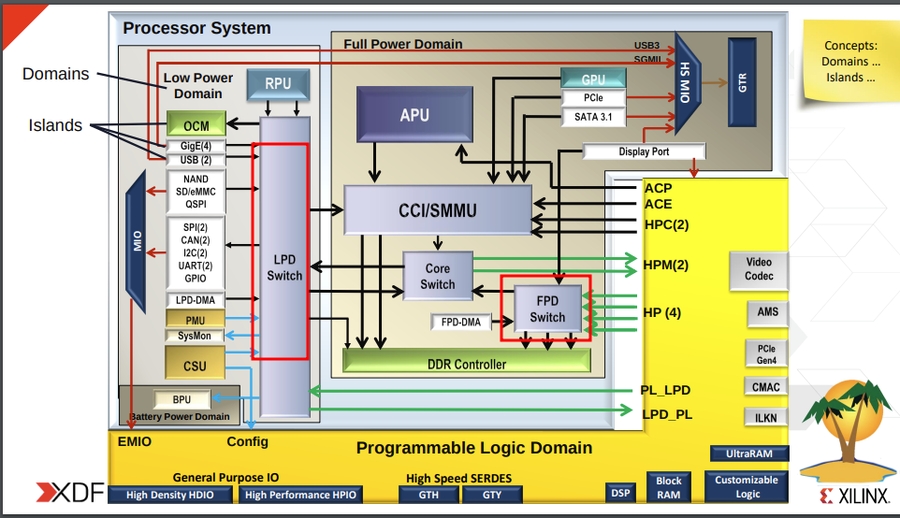
ZYNQ UltraScale+ 是一种SoC设计,主要包含下面的片上系统:
Quad-core Arm® Cortex™-A53-based Application Processing Unit (APU)
Dual-core Arm Cortex-R5F-based Real-Time Processing Unit (RPU)
Arm Mali™-400 MP2 based Graphics Processing Unit (GPU)
Dedicated Platform Management Unit (PMU) and Configuration Security Unit (CSU)
List of high-speed peripherals, including display port and SATA
请重点关注一下以上的加粗的单元,可能启动的时候会做一些关于平台级的操作,否则导致一些单元不正常。
关于启动流程方面,我们应该兼顾:
如何集成和加载bootloaders
baremental环境app(APU/RPU)
runtime环境,Linux OS(以QSPI,SD,JTAG等方式启动)
一些关键点,我们不应该错过:
系统软件:FSBL,PMU 固件,U-Boot,TF-A
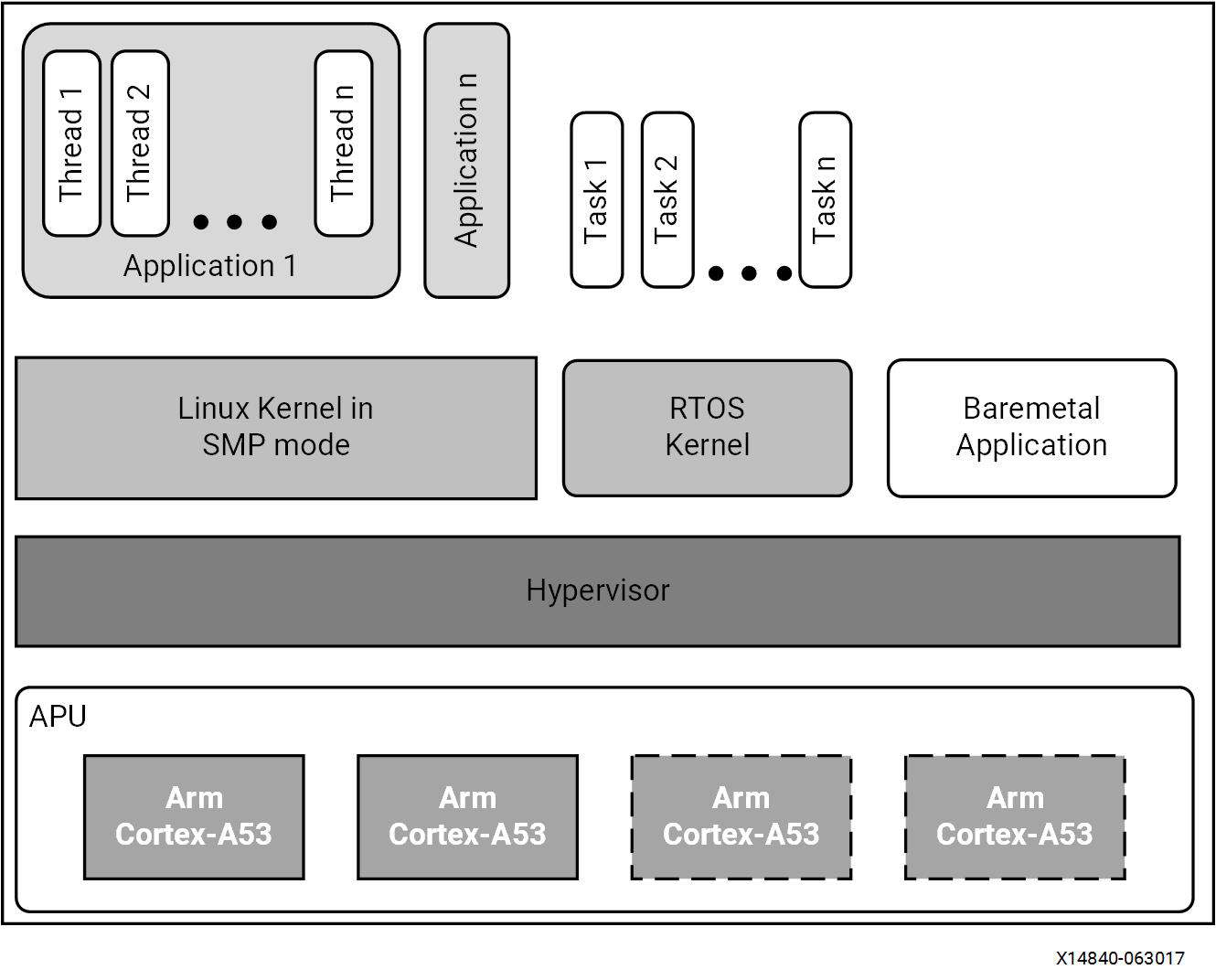
APU : 为APU配置SMP Linux
RPU (realtime-processing-unit):同步为PRU配置baremental
创建boot image : APU -> PRU lockstep
创建和加载 secure boot image (重点关注,看看对于secure boot的要求)
创建boot image的工具
在Vitis IDE中的Create Boot Image wizard
命令行工具Bootgen (bootgen tool)
note, 原则上,bootgen能够用一种合适的方式集成bitfile和软件
note, bootgen能够配置安全选项,甚至可以指定密码学的key
我们可以在这个地方找到比较详细的设计 https://docs.xilinx.com/r/en-US/ug1137-zynq-ultrascale-mpsoc-swdev/Bare-Metal-Software-Stack 里面包含系统启动和配置的详细设计。我们在后面的章节展开这部分内容。
关于bootgen user的内容参考:https://docs.xilinx.com/r/en-US/ug1283-bootgen-user-guide/Introduction 。
1. 启动流程 High-Level
从ZYNQ的一些设计中,他意图:
以不同的方式启动(QSPI,SD,甚至一个host工具Device Firmware Upgrade utility,NAND flash)
以不同的模式启动(安全和非安全模式)
多级启动(multi-staged booting)
以下是ZYNQ完整的启动流程:
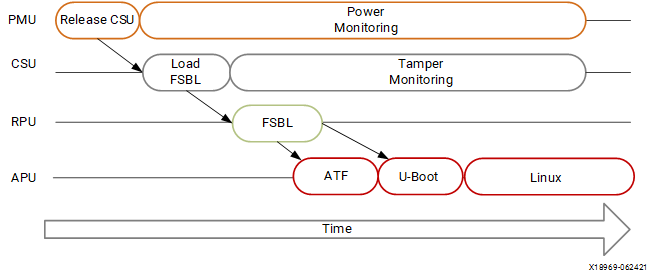
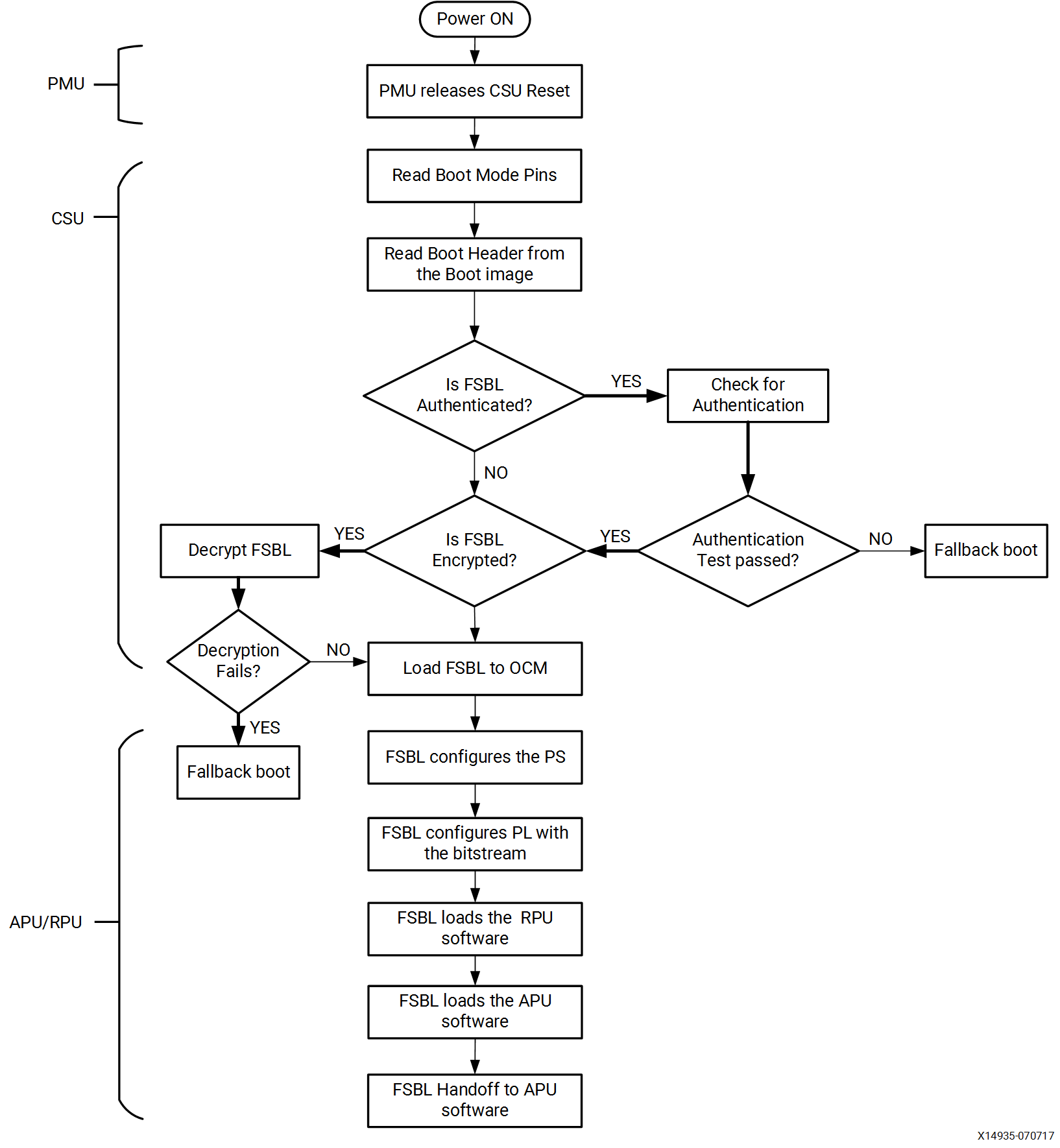
PMU(platform management unit)和CSU(configuration security unit)用于管理和执行多级启动。在两个单元中,我们可以配置安全启动和非安全启动,(这里界定安全和非安全在于image上面,使用authenticated boot image视为安全启动)。
PMU多插一嘴,PMU用于释放CSU;CSU用于加载FSBL(第一级引导)。RPU等同于FSBL,APU就是ATF和U-Boot还有Linux这些了。对于这些启动流程,在ZYNQ上是有明确定义的:
Pre-configuration stage: PMU来执行该阶段,在SoC上设定PMU ROM,执行这个ROM的程序来初始化系统。PMU主要处理所有的单元的复位和唤醒工作。
Configuration stage:这个阶段主要是为PS加载FSBL程序到on-chip RAM(OCM)。
在这个阶段就开始分安全和非安全模式了。
通过boot的header,我们可以执行FSBL在CortexR5F上面或者是Cortex-A53上面(cortexr5f也支持lock同步模式)
Post-configuration stage:FSBL在开始执行之后,fpga进入到post configuration stage。
1.2. non-secure boot flow
我们来说一下非安全的启动流程,PMU首先会释放处于reset中的CSU单元,之后就会进入长期的PMU power server模式;当CSU从reset状态释放之后,CSU会把FSBL的程序加载到OCM中。PMU固件从PMU的RAM运行,同时并行地运行在OCM中的CSU。FSBL在APU或者RPU上面运行的,FSBL从APU/RPU运行到ATF。UBOOT和linux实在APU上面运行的。其他的引导配置允许RPU完全独立于APU运行,也可以耦合。
1.3. secure boot flow
MU首先会释放处于reset中的CSU单元,之后就会进入长期的PMU power server模式;当CSU从reset状态释放之后,到此都是和nonsecure一致。CSU从reset状态还原回来之后,来检查是否进行secure check,这个secure check(authentication check)是否是能是由FSBL或者这user的app来决定的。因此,我们有两个思路来启动secure boot,一个是在FSBL中,或者开发这个user 的app(baremental的app)。
ZYNQ有对CSU有行为准则的规定:
首先需要进行身份检查,一切的检查都是在身份检查的基础上再言其他;
如果csu检测出分区已经被加密,csu执行解密操作,解密之后的fsbl程序需要加载到ocm中。
For more information on CSU, see the Configuration Security Unit section.
1.4. boot image 创建
ZYNQ提供一个bootgen的工具,这个工具主要就是把二进制文件缝合在一起,还可以配置一些属性、特性和参数。更重要的是,secure boot的使能也是通过bootgen tool,喂给bootgen tool公钥私钥。bootgen tool还能提供指定目的地址,对齐的需求。(关于认证流程和密钥管理的在Using HSM Mode中讨论 https://docs.xilinx.com/r/en-US/ug1283-bootgen-user-guide/Encryption-and-Authentication )。 bootgen还可以同步输出一些hash文件,这些hash文件可以使用私钥进行签名做一些离线验证。最后bootgen工具会把所有的二进制文件都打包成为image,并且加入了描述的头文件(包含所有的分区)
我们可以配置分区加密性和认证性使用bootgen。输出的文件可以直接写入到boot flash的分区里面(格式已经做了匹配)。
ZYNQ提供了GUI的配置和cmd的配置,cmd的配置更丰富,GUI只不过是cmd的一个子集。cmd工具通常被集成到脚本中使用。
bootgen工具由一个扩展名为*.bif的引导映像格式(bif)驱动。与SoC一起,Bootgen能够为FPGA和以后的FPGA加密和验证分区,如FPGA支持中所述。除了定义引导映像行为的受支持命令和属性之外,还有一些实用程序可以帮助您使用Bootgen。Bootgen代码现在可以在Github上使用( https://github.com/Xilinx/bootgen )。
1.5 boot mode
bootmode的具体支持和配置方法如下: https://docs.xilinx.com/r/en-US/ug1085-zynq-ultrascale-trm/Boot-Modes
1.5.1 QSPI24 and QSPI32 Boot Modes
The QSPI24 and QSPI32 boot modes support the following:
x1, x2, and x4 read modes for single Quad SPI flash memory 24 (QSPI24) and single Quad SPI flash memory 32 (QSPI32)
x8 read mode for dual QSPI.
Image search for MultiBoot
I/O mode for BSP drivers (no support in FSBL)
使用SPI需要注意BOOTROM寻址大小问题:bootrom寻址空间256M-bit x 8;在QSPI24和QSPI32的引导模式, 主意啊,这个设备 需要 < 128M-bit。设计多级images主要是为了让内存小于128M-bit。
Note: QSPI dual stacked (x8) boot is not supported. Only QSPI Single Transmission Rate (STR) is supported**. Single Quad-SPI memory (x1, x2, and x4) is the only boot mode that supports execute-in-place (XIP)**.
生成QSPI需要的image,在使用gentool之前,需要准备以下文件:
An FSBL ELF
二级引导 secondary boot loader(SBL),例如uboot,或者是Cortex-RF/R-1或者是Cortex-A53的裸机程序(ELF)
如果要使能secure boot 开发者手册中需要有: https://docs.xilinx.com/r/en-US/ug1137-zynq-ultrascale-mpsoc-swdev/BIF-File-with-an-Operational-Key
1.5.2 SD Boot Mode
ZYNQ可以通过SD卡进行引导:
FAT 16/32 文件系统来读boot images;
多级引导最大的文件数8192;
Note: exFAT is 不支持 for SD boot in FSBL and U-Boot.
下面是SD卡的引导流程:
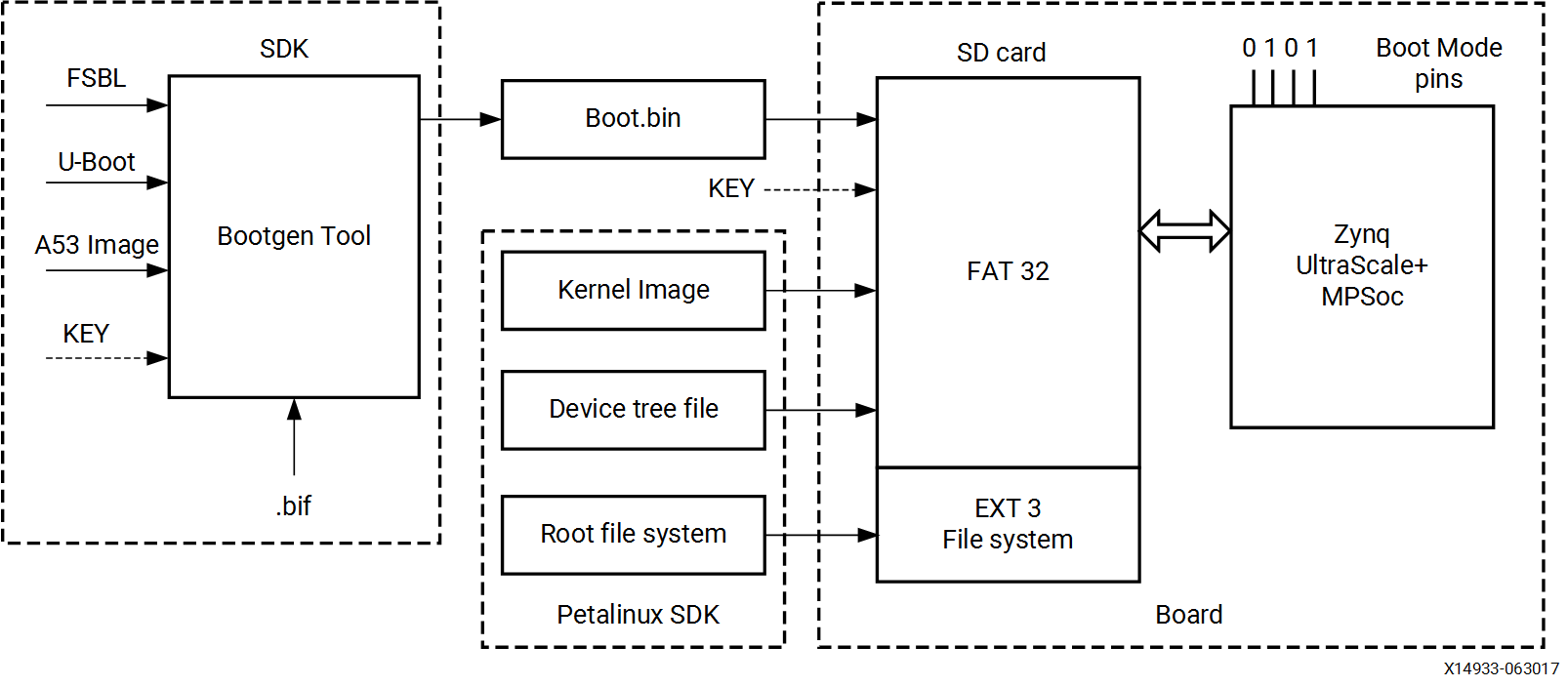
因此,我们创建一个SD的引导image,需要提供和下面的文件给bootgen:
FSBL ELF文件
Cortex-R5f或者Cortex-A3的ELF
(可选)验证和加密的key
bootgen tool会产生boot.bin文件,可以把boot.bin文件用读卡器直接写入SD卡中(投过文件系统而不是RAW write)
对于PetaLinux,需要做:
编译Linux kernel的image,设备树文件,根文件系统
文件复制到SD card中。
Note, 格式化后的SD卡包含引导。bin、内核映像和FAT32分区中的设备树文件;根文件系统驻留在EXT 4分区中。
!!!!!! Important: To boot from SD1, configure the boot pins to
0x5. To boot from SD0, configure the boot pins to0x3.To boot from SD with a level shifter, configure the boot pins to0xE.
1.5.3 eMMC18 Boot Mode
eMMC18 boot (version 4.5) supports the following:
FAT 16/32文件系统存储images文件。
同SD一样,文件限制8192。
几乎和SD卡一模一样,除了存储媒介不同。 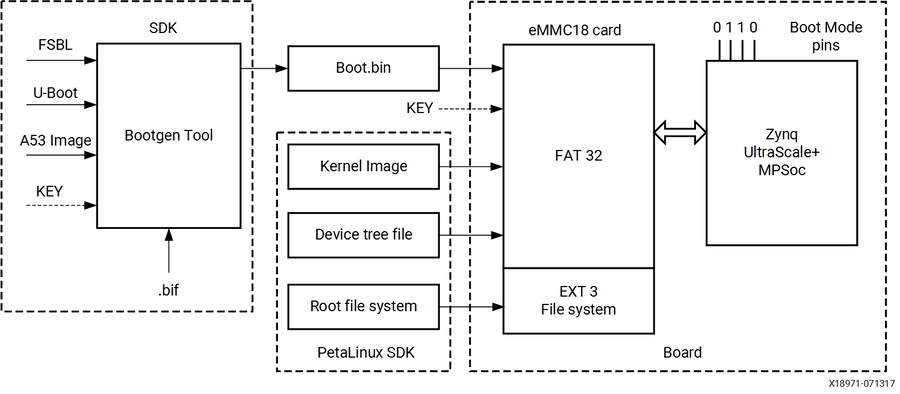
FSBL ELF文件
Cortex-R5f或者Cortex-A3的ELF
(可选)验证和加密的key
bootgen tool会产生boot.bin文件,可以把boot.bin文件用读卡器直接写入SD卡中(投过文件系统而不是RAW write)
对于PetaLinux,需要做:
编译Linux kernel的image,设备树文件,根文件系统
文件复制到SD card中。
Note, 格式化后的SD卡包含引导。bin、内核映像和FAT32分区中的设备树文件;根文件系统驻留在EXT 4分区中。
1.5.4 NAND flash Boot Mode
NAND flash的启动模式只支持8 bit 宽度读取引导images。
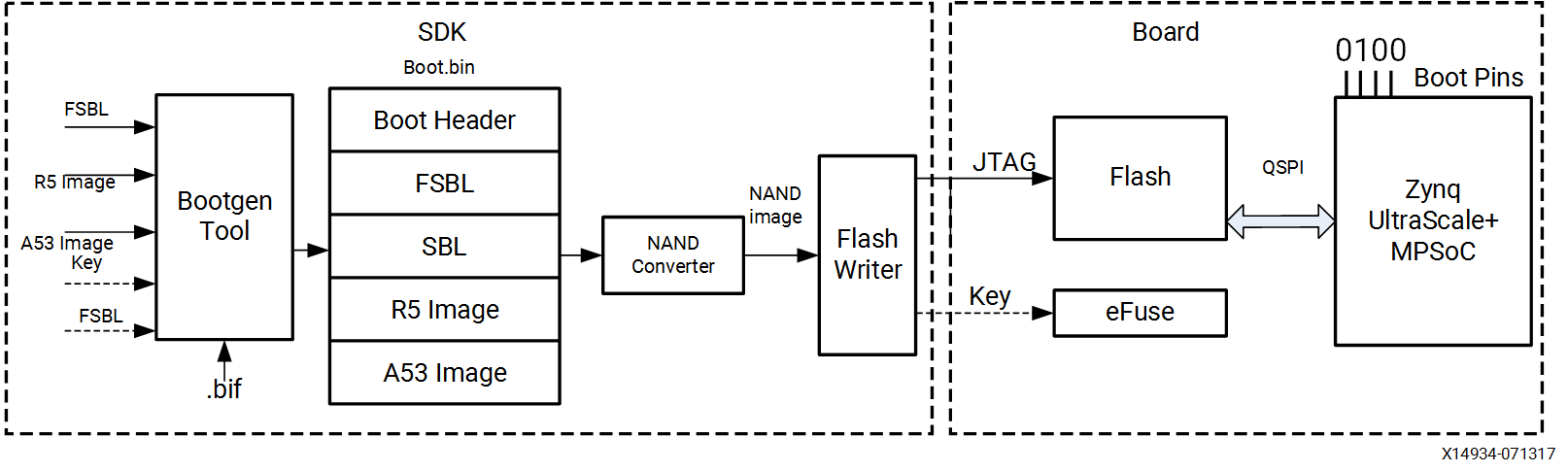
FSBL ELF文件
Cortex-R5f或者Cortex-A3的ELF
(可选)验证和加密的key
需要注意的事,boot.bin需要经过NAND Converter转换为NAND image( flash writer),看图中这部分应该是集中在SDK中。最后通过JTAG的方式把 boot.bin写入 FLASH,而密钥需要写入efuse。
!!!! Important: To boot from NAND, configure boot pins to
0x4.
1.5.5 JTAG boot mode
JTAG是一个权限十分巨大的启动模式,我们可以手动下载任何软件image到PS中,使用JTAG。而对于ZYNQ,secure boot无法支持JTAG启动模式。
1.5.6 USB boot mode
仅支持USB2.0模式。USB模式支持非安全和不安全的启动。USB启动不支持缺乏DDR的系统,multiboot/fallback image/XIP也是不支持的。
Note: USB boot mode is disabled by default in FSBL. To enable the USB boot mode, configure the FSBL_USB_EXCLUDE_VAL to 0 in xfsbl_config.h file.
这部分暂时不做深入研究,有真正的需求之后,再去做。
1.5.7 Secondary boot mode
https://xilinx-wiki.atlassian.net/wiki/spaces/A/pages/18842019/Zynq+UltraScale+FSBL#ZynqUltraScale%2BFSBL-WhatisSecondaryBootmode%3F
需要关注的点是,ZYNQ有两个boot devices,主引导设备和辅助引导设备。主引导模式是用来加载FSBL和PMU FW加载到BOOTROM里面;辅助引导设备是用来加载所有其他分区的引导设备。辅助引导设备支持QSPI/SD/EMMC的启动模式。
但需要注意:
默认情况,辅助引导设备和主引到设备相同,除非在bif文件中指定 例如
[boot_device] qspi24,这个FSBL将会从引导设备加载,但所有其他分区将从辅助引导设备qspi24引导。辅助引导需要两个bif文件,因此需要两个引导映像。第一bit file包含bootrom加载的分区,以及指定辅助引导模式[boot_device] qspi24。第二个bif file包含FSBL分区,然后是FSBL加载的所有的分区。“bootgen-bif_help boot_device”将列出所有辅助引导选项。
如果指定了辅助引导模式,它应该与主引导设备不同。例如,如果QSPI32是主引导模式,则QSPI24不能是辅助引导模式。相反,您可以使用SD0、eMMC、SD1、SD1 ls、NAND、USB作为辅助引导模式。所有引导设备的组合都支持作为主引导设备和辅助引导设备。
上面的链接提供了主引导设备和usb作为辅助引导的示例的bif文件。
2. 启动流程 Low-Level
LowLevel是相对细节的部分,暂时不深入的code研究细节,只是了解每个过程都做了什么工作。在High-Level中,我们知道ZYNQ存在的几个单元:
PMU用于处理pre-boot的一些任务 :
执行ROM,配置power状态、初始化RAMs、测试环境和寄存器;
引导CSU(releases CSU reset)
CSU用于处理Configuration Stage的任务:
加载FSBL到OCM
既然涉及FSBL,那么就有
ecure boot的事情了。
AP阶段开始正常的AP引导(post-configration stage)
2.1 PMU and CSU seq
下面的表格可以表示 pre-boot阶段的启动模式:
Initialize MicroBlaze™ processor. Capture key states.
Scan, and clear LPD and FPD.
Initialize the System Monitor.
Initialize the PLL used for MBIST clocks.
Zero out the PMU RAM.
Validate the PLL. Configure the MBIST clock.
Validate the power supply.
Repair FPD memory (if required).
Zeroize the LPD and FPD and initialize memory self-test.
Power-down any disabled IPs.
Either release CSU or enter error state.
Enter service mode.
一旦CSU的reset引脚被释放,PMU就执行CSU的bootrom,并且执行下面的任务序列:
初始化OCM
监测引导模式(通过读取boot mode寄存器,这个在ZYNQ上电时候根据启动模式配置自动写入)
CSU继续FSBL的加载,与此同时PMU也可以执行PMU firmware(可选)。
关于FPD和LPD需要介绍一下,这部分是电源域:
LPD(Contains the ARM Cortex-R5 real-time processor unit (RPU), theplatform management unit (PMU), and the configuration security unit (CSU), aswell as the remaining on-chip peripherals.)要先于FPD(Contains the ARM Cortex-A53application processor unit (APU) as well as a number of peripherals typicallyused by the APU.)
2.1.2 Disabling FPD in Boot Sequence
Perform the following to avoid an FPD lockout, where FPD Power is applied momentarily:
Apply the power until the completion of bootROM execution.
To power down the FP during FSBL execution, set FPD bit '22' of PMU_GLOBAL REQ_PWRDWN_STATUS register.
To bring the FP domain up in a later stage of the boot process, set the PMU_GLOBAL REQ_PWRUP_STATUS bit to '22’.
Perform the following in cases where the FPD power is not applied before the FSBL boots
Power up the R5.
A register is set indicating the FPD is locked pending POR as the reset or clear sequence cannot execute on the FPD.
R5 can read the FP locked status from PMU_GLOBAL REQ_ISO_STATUS register bit ‘4’.
At this stage, PMU_GLOBAL REQ_PWRUP_STATUS bit '22' will not be set.
To bring the FPD node back up, power must be supplied to the node and a POR needs to be issued.
2.1.3 Setting FSBL Compilation Flags
You can set compilation flags using the C/C++ settings in the Vitis FSBL project, as shown in the following figure:
Note: There is no need to change any of the FSBL source files or header files to include these flags.
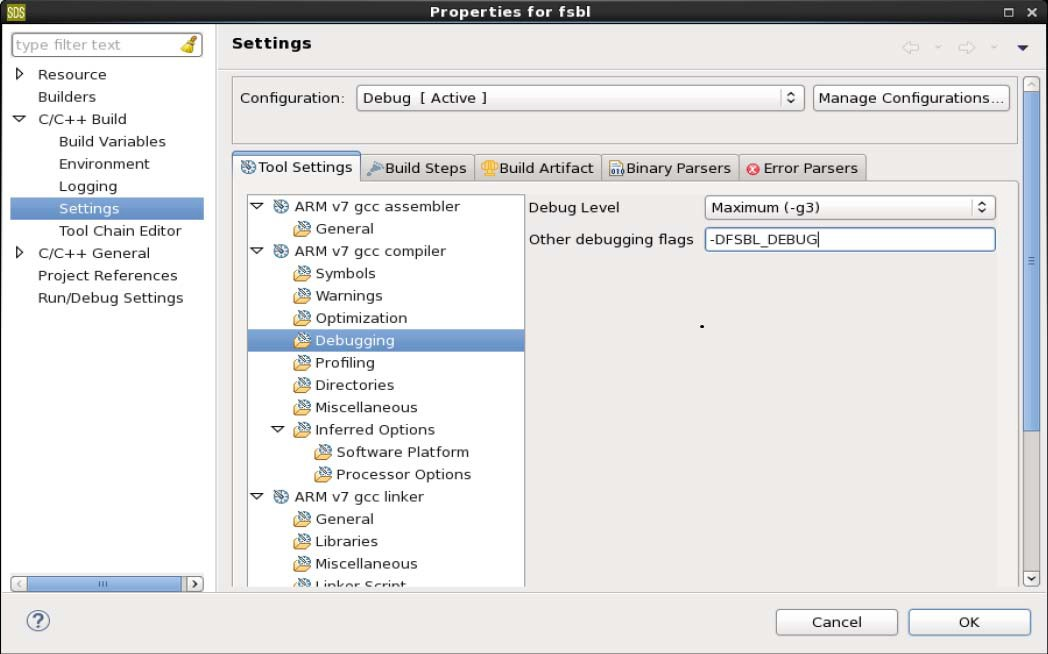
编译选项提供一个shrink size的功能:
https://xilinx-wiki.atlassian.net/wiki/spaces/A/pages/18842019/Zynq%2BUltraScale%2BFSBL#ZynqUltraScale%2BFSBL-I%E2%80%99munabletobuildFSBLduetosizeissues%2ChowcanIreduceitsfootprint%3F
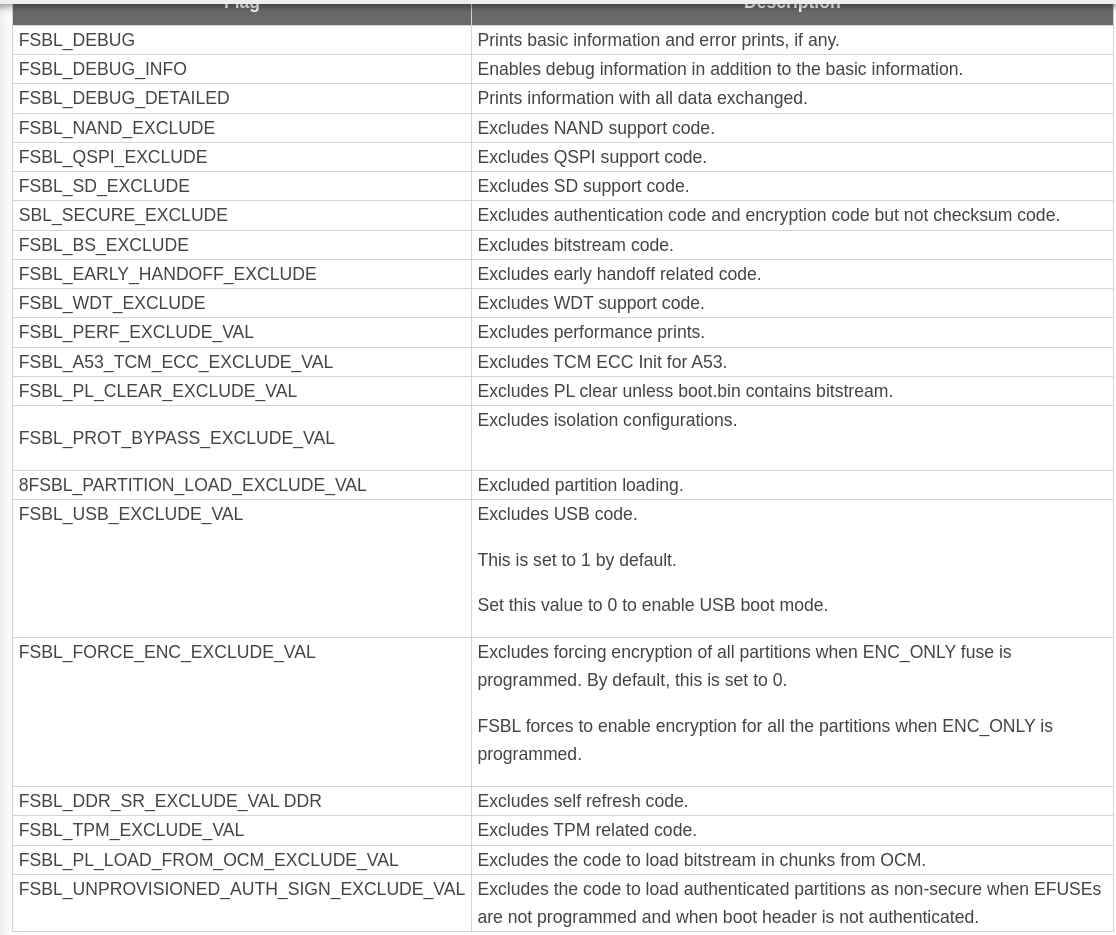
关于debug调试输出有以下编译选项:
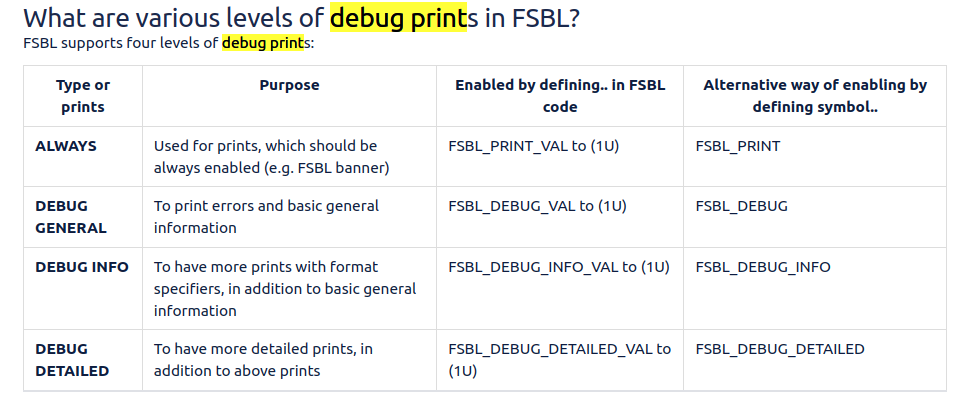
2.1.4 Fallback and MultiBoot Flow (golden image search)
根据上面的流程图,无论是引导失败还是secure boot失败,都会走向fallback的流程,ZYNQ设计fallback的功能,我们可以根据CSU的配置,让CSU来寻找正确的image来加载,查找规则如下:
bootrom寻找一个正确的image是通过image id 一个字符串来寻找的(这个id在flash的32KB偏移量的位置)
找到正确的索引之后,来验证header的checksum值;
如果checksum是正确的,bootrom就会加载这个image
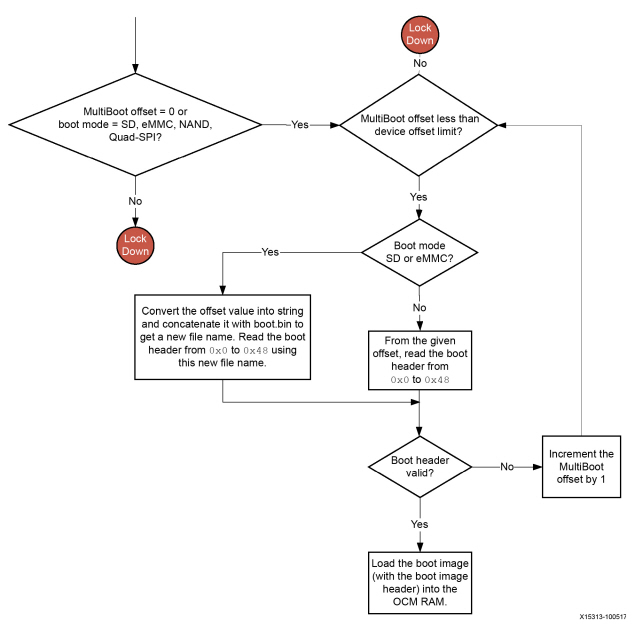
因此,要实现这个技术就必然允许超过一个image在flash中。除此之外还要在Multi boot中进行配置:
In MultiBoot:
CSU ROM or FSBL or the user application must initiate the boot image search to choose a different image from which to boot.
To initiate this image search, CSU ROM or FSBL updates the MultiBoot offset to point to the intended boot image, and generates a soft reset by writing into the CRL_APB register.
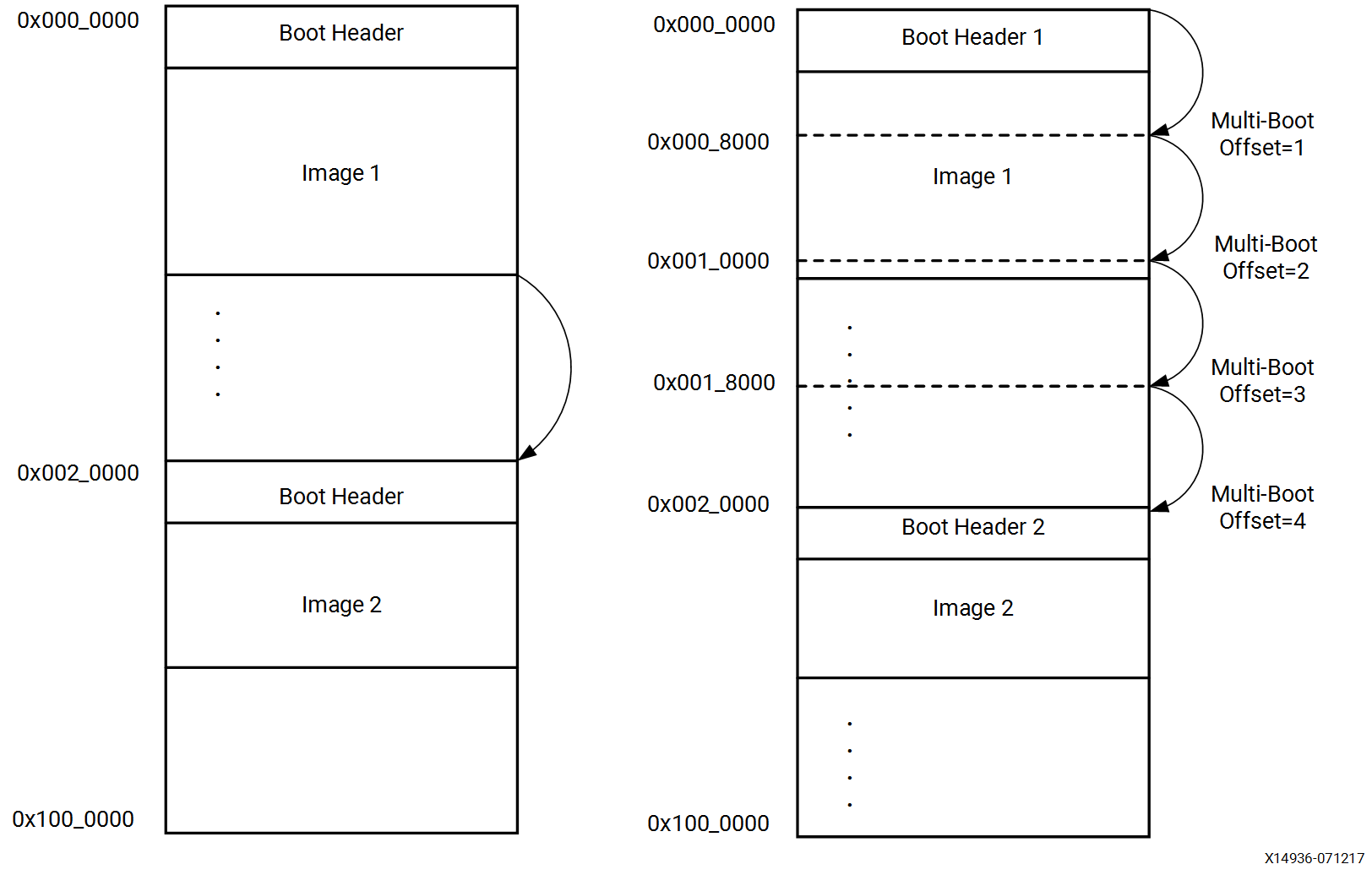
这个过程可以描述为:
最开始,CSU bootrom加载0x0的boot image;
如果这个image做secure boot失败或者损坏,CSU bootrom会搜寻下一个image在32kb的位置(0x0000_8000)的位置。
如果在这个位置并没有一个识别头,或者CSU bootrom继续向下一个offset搜寻(0x0001_8000)的位置。
直到找到一个正确的image或者到了寻找的地址范围。
范围如下:
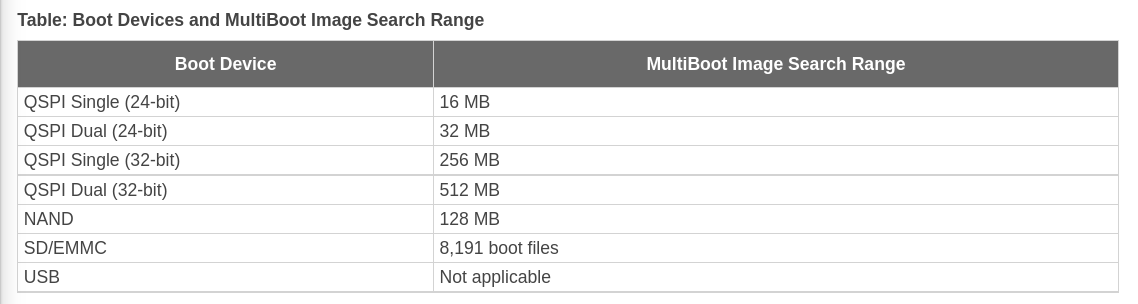
无论是non-secure 或者secure的都是支持fallback规则。
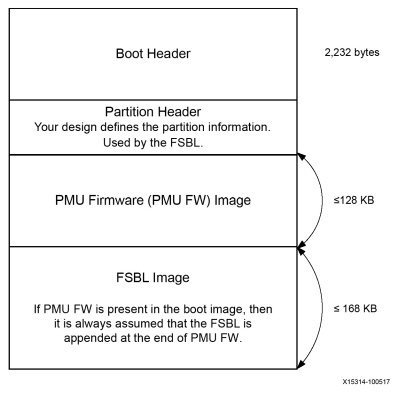
boot image 的格式:
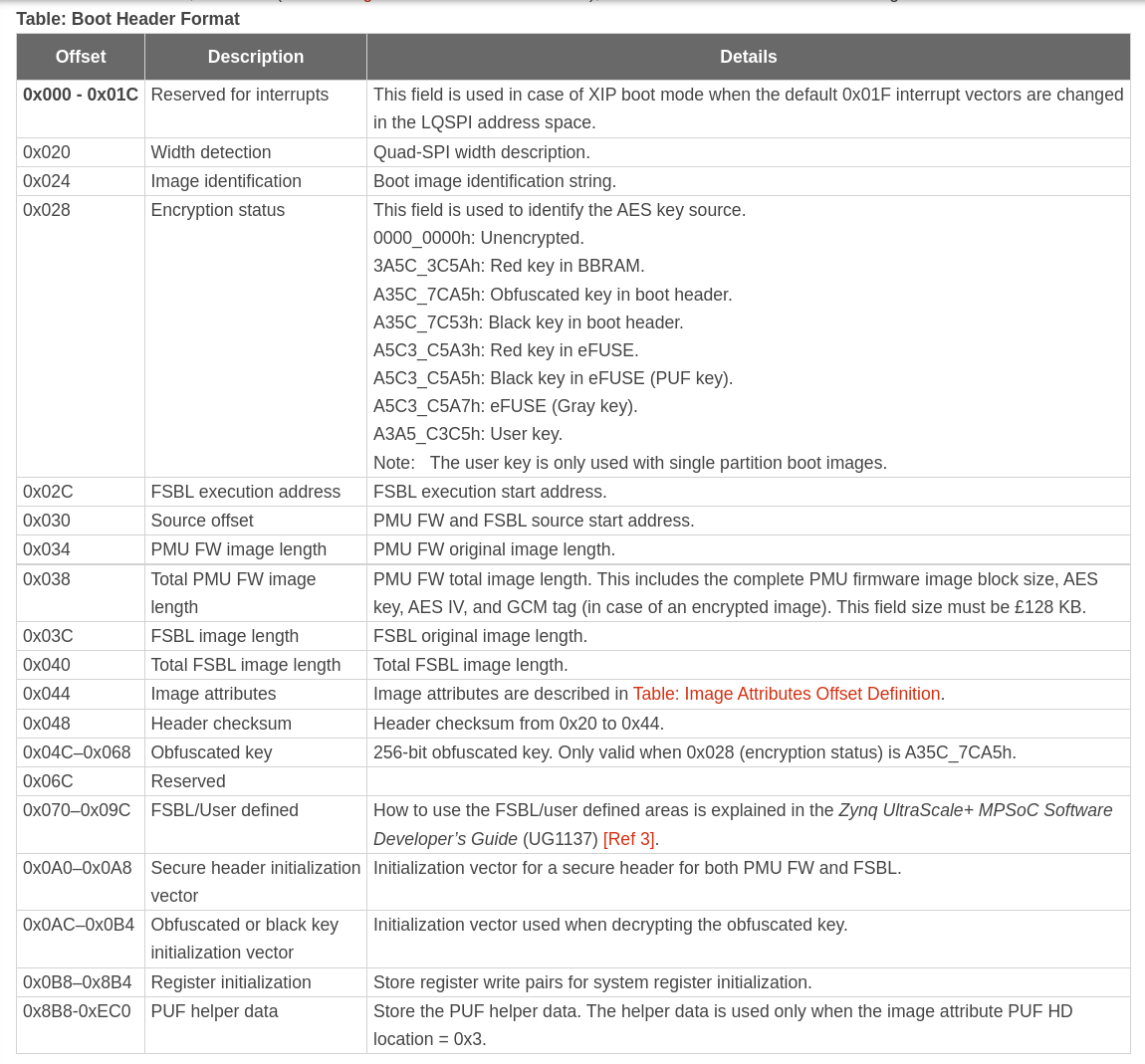
header的格式:
2.2 FSBL stage
PMU和CSU在软件上程序员只是需要关注原理和配置(模式)即可,进入到FSBL阶段,就需要程序员来进行编译和程序的修改了。
FSBL在认证和解密之后(如果是能了secure boot),此时FSBL被CSU加载进入OCM中,并且从CSU中接手执行权限。FSBL使用FPGA的bitstream进行配置,并且FSBL需要加载Standalone(SA,裸机程序)或SSBL(Second stage boot loader)的image从(NAND/SD/EMMC/QSPI)加载到RAM中(DDR/TCM/OCM)。FSBL需要将R5F核或者A53核解除复位状态。FSBL同样支持多个分区(每一个分区可以是一个image,或者一个bitstream)。如果使能secure boot,每一个分区需要被认证或者解密。
注意:如果在创建一个FSBL过程中,我们始终有一种意识是OCM的大小仅仅256kb,除去CSU使用的部分,给我们留下的大小大概是170kb。然而,使用USB启动模式的时候要确认PMU firmware是被FSBL加载而不是CSU 的bootrom。因为usb的超过了CSU的打消了。
在未加密的情况下,用户可以加载bitstream:
By default, the FSBL_PL_LOAD_FROM_OCM_EXCLUDE_VAL value is set to 0 in xfsbl_config.h, making the bitstream copy and load from DDR in the non-encrypted cases.
By setting the FSBL_PL_LOAD_FROM_OCM_EXCLUDE_VAL value to 1, the user can ensure that bitstream is loaded from OCM in chunks and not from DDR
if DDR is not present in the design, the bitstream is loaded from OCM irrespective of the FSBL_PL_LOAD_FROM_OCM_EXCLUDE_VAL value.
2.2.1 create FSBL project
这部分在文档中介绍了:
To create a new Zynq UltraScale+ MPSoC FSBL application in the Vitis software platform, do the following:
Click File > New > Application Project. The New Application Project dialog box appears.
In the Project Name field, type a name for the new project.
Select the location for the project. To use the default location as displayed in the Location field, leave the Use default location check box selected. Otherwise, click to deselect the check box, then type or browse to the directory location.
Select Create a new platform from hardware (XSA). The Vitis IDE lists the all the available pre-defined hardware designs.
Select any one hardware design from the list and click Next.
From the CPU drop-down list, select the processor for which you want to build the application. This is an important step when there are multiple processors in your design. In this case you can either select psu_cortexa53_0 or psu_cortexr5_0.
Select your preferred language: C.
Select an OS for the targeted application.
Click Next.
In the Templates dialog box, select the Zynq UltraScale+ MPSoC FSBL template.
Click Finish to create your application project and board support package (if it does not exist).
请注意第6步骤的多核场景,如果在应用中使能了多核的场景,我们在boot中也该做相应的配置,否则可能会block多核的正常使用。
2.2.2 FSBL LowLevel
一个合格的FSBL,必须有以下的能力:
FSBL operation includes the following four stages:
Initialization
Boot device initialization
Partition loading
Handoff
这部分我们暂时不研究了。
3. Golden image example
Golden image是存在非易失性存储上的备用的image,当主引导image损坏时,ZYNQ的Multiboot机制可以引导该image。其设计目的是:在 ZYNQ 产品出厂后,如果要更新功能,像手机那样的下载更新,如果更新失败就会变成“砖”。Multiboot 的存在就是为了解决这一问题。将 ZYNQ 产品的出厂引导文件放在 QSPI FLASH / SD Card的可引导的末端位置,这时的出厂引导文件就做 Golden Image,后面更新功能的时候将更新的引导文件放在 QSPI FLASH / SD Card的可引导的前端,也就是说 ZYNQ 启动后,先检索到更新的引导文件,然后引导其启动,如果该文件更新失败,就会从检索到的 Golden Image(出厂引导文件)启动,免得更新失败造成产品不可用。
根据2.1.4小节,可以总结为ZYNQ的multiboot机制有以下特点:
Golden Image Search 当在闪存的底部(起始位置)没有找到有效的头文件时,BootROM 就会发起 Search 请求。BootROM 将在每 32KB 的偏移量处开始搜索一个有效的头。这种机制很慢,但很可靠。
BootROM Multiboot 这是由 FSBL 发起的,也就是 user。如果 BootROM 找到了一个有效的头文件并交给 FSBL,那么 FSBL 可以加载 Multiboot 寄存器并发出软复位。软复位后,BootROM 将使用 Multiboot 寄存器的地址来读取 BootROM 头文件。例如,当用户想要运行自检和诊断,然后跳转到实际的应用程序时,就会使用这种机制。
FSBL Fallback 为了从错误条件中恢复,FSBL 做了一个回退(Fallback),使 BootROM 能够加载另一个可引导镜像 (最初出现并处于已知良好状态的 golden image),如果该镜像存在于闪存中。FSBL 更新一个 Multiboot 寄存器并进行软复位,以便 BootROM 执行并加载下一个当前有效的镜像。无论是否软复位,FSBL 都可能发生回退。
3.1 使用 FSBL Fallback 来进行 Multiboot(non-sec)
3.1.1 用例目的
制作一个non-sec的用例来触发ZYNQ的fallback流程以启动golden image;了解golden image的制作过程;对fallback流程进行验证。
3.1.2 实验方法
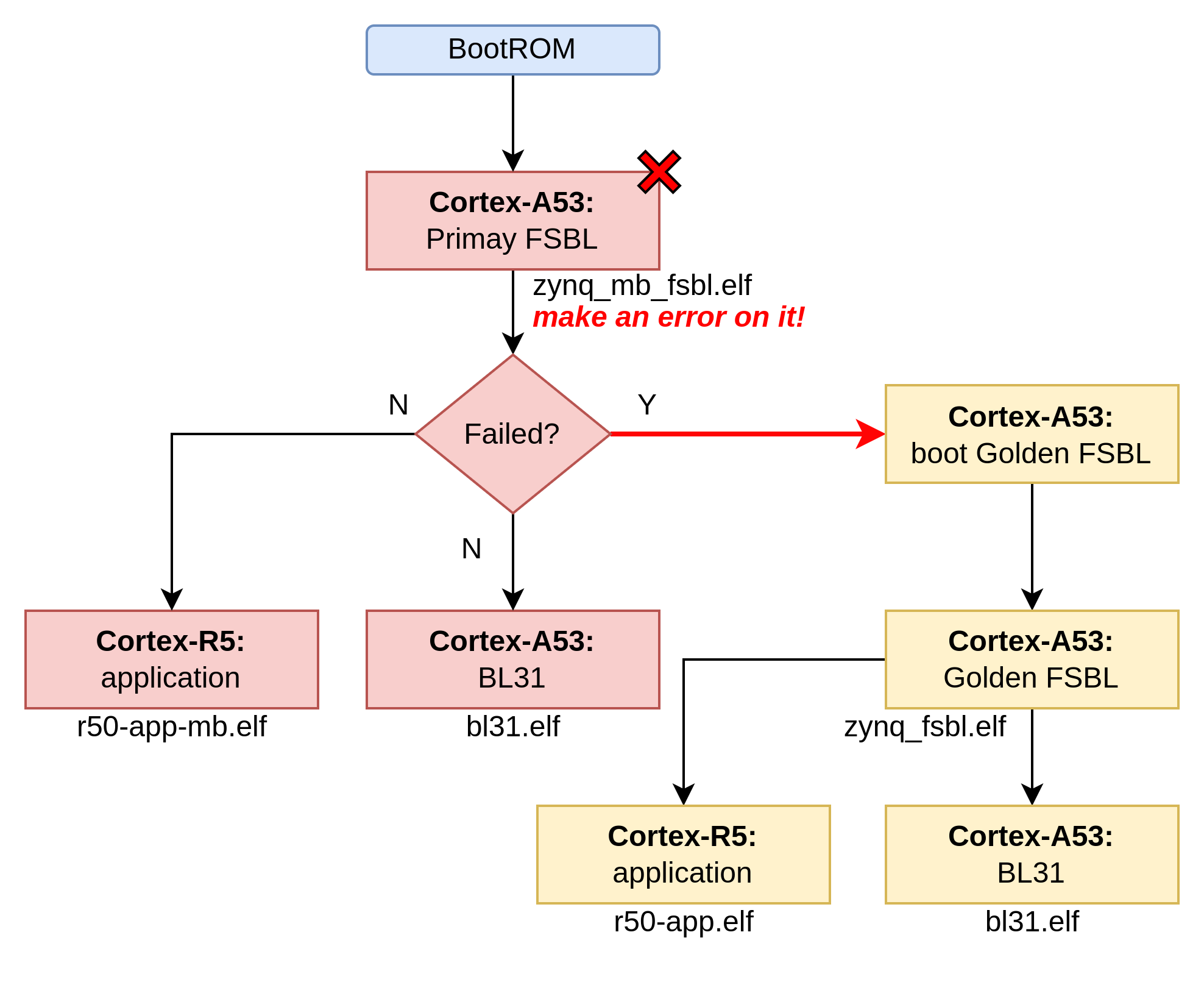
准备两路引导,一路primary引导,另一路是golden引导。在primay引导中,故意制造一个错误,让其引导失败返回,验证ZYNQ是否进入golden image路径。
在primary引导中:
设定
zynq_mb_fsbl.elf文件为primary FSBL (故障固件);设定
r50-app-mb.elf为 cortex-R5核心的普通应用程序(设定输出log为"primary image",以此识别当前引导所在路径primary image);设定
bl31.elf为 TF-A 引导固件。
在Golden引导中:
设定
zynq_fsbl.elf文件为primary FSBL (好用的固件);设定
r50-app.elf为 cortex-R5核心的普通应用程序(设定输出log为"golden image",以此识别当前引导所在路径为golden image);设定
bl31.elf为 TF-A 引导固件(以primary为同一个文件)。
实验判定:当ZYNQ启动之后,串口输出log为"golden image" 证明启动进入goledn image成功。
3.1.3 实验过程
我们要生成:
zynq_mb_fsbl.elf (故障的fsbl引导)
r50-app-mb.elf (输出log为 primary image的应用)
zynq_fsbl.elf (完整的fsbl引导)
r50-app.elf (输出log为 golden image的应用)
3.1.3.1 创建vitis FSBL工程
在vitis创建FSBL工程,以生成:
zynq_mb_fsbl.elf (故障的fsbl引导)
zynq_fsbl.elf (完整的fsbl引导)
生成zynq_fsbl.elf
zynq_fsbl是一个完整的golden image,因此不需要对工程进行修改,直接编译,编译出的二进制elf文件命名为:zynq_fsbl.elf 留用。
生成zynq_mb_fsbl.elf
接着,我们需要生成一个故障的zynq_mb_fsbl.elf,可以在其源代码中,修改某个节点返回值,插桩制造一个错误。
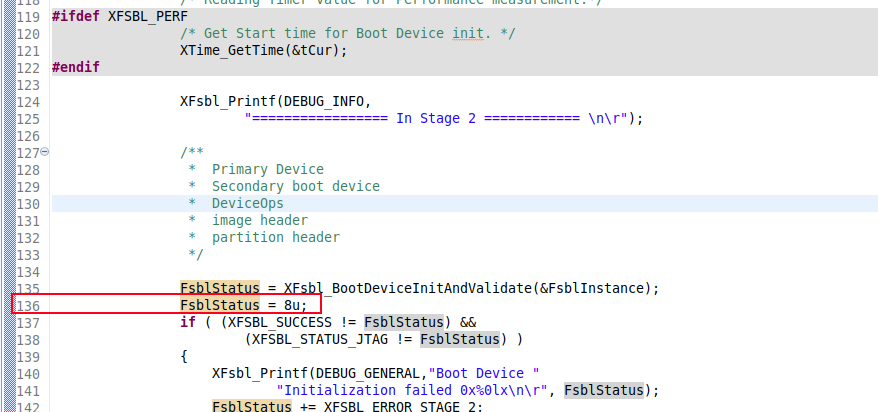
我这里在136行,故意插入一个错误的代码,让其进入Fallback流程。然后对项目进行编译。生成的编译之后的elf文件,命名为:zynq_mb_fsbl.elf 留用。
3.1.3.2 创建Cortex-R5 hello world 应用
在vitis创建Cortex-R5工程,以生成:
r50-app-mb.elf (输出log为 primary image的应用)
r50-app.elf (输出log为 golden image的应用)
r50-app.elf
在工程中修改main函数中的log输出,标识是golden image:
编译出来的elf文件,重命名为r50-app.elf 留用。
r50-app-mb.elf
在工程中修改main函数中的log输出,标识是primary image:
编译出来的elf文件,重命名为r50-app-mb.elf 留用。
3.1.3.3 建立primary引导
该步骤需要使用bootgen工具,其bif为:
生成命令:
3.1.3.4 建立golden引导
该步骤需要使用bootgen工具,其bif为:
生成命令:
3.1.3.5 拷贝到SD卡 boot分区
boot.bin 和 boot0001.bin 和 boot0002.bin 复制到SD卡的boot分区,大功告成。
3.1.3 实验结果
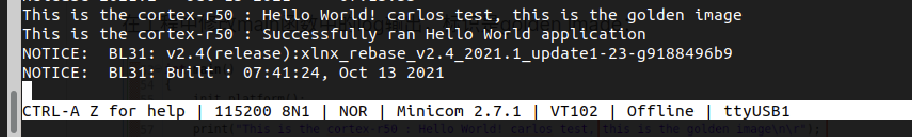
3.2 使用 FSBL Fallback 来进行 Multiboot(secure)
基于3.1 non-sec的实验,现在对所有的image进行加密,需要注意两点:
Multiboot and fallback boot images(boot.bin, boot000x.bin) should be made with using same key in encryption for Secure boot mode.
Multiboot and fallback boot images(boot.bin, boot000x.bin) should be made with using same key in authentication for Secure boot mode.
我们的images还是利用3.1实验中的images:
zynq_mb_fsbl.elf (故障的fsbl引导)
r50-app-mb.elf (输出log为 primary image的应用)
zynq_fsbl.elf (完整的fsbl引导)
r50-app.elf (输出log为 golden image的应用)
除此之外还需要准备加密的key和签名的私钥:
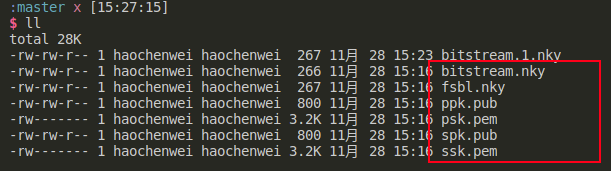
3.2.1 实验步骤
3.2.1.1 建立primary引导
该步骤需要使用bootgen工具,其bif为:
生成命令:
3.2.1.2 建立golden引导
该步骤需要使用bootgen工具,其bif为:
生成命令:
3.2.1.3 拷贝到SD卡 boot分区
boot.bin 和 boot0001.bin 和 boot0002.bin 复制到SD卡的boot分区,大功告成。
3.2.2 实验结果
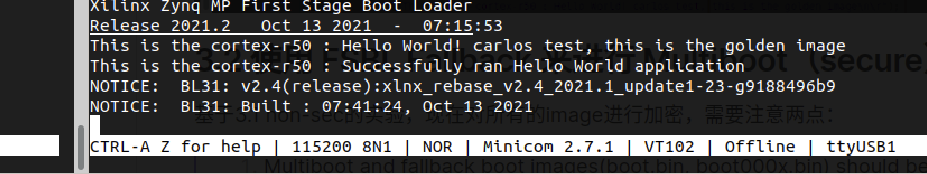
3.3 总结
到此,我们完成了non-sec和sec的Golden image的实验。
Ref
最后更新于