[LS104x] secure boot
1. secure boot overview
1.1 introduction
NXP的secure boot流程被分为多个阶段,严格按照TF-A的规则使用,分为BL1, BL2 (at EL3), BL31, BL32, BL33。secure boot的image验证是使用各自的image header完成。
image header有两类:
CSF headers (NXP Chain of Trust) 参考:Code signing tool.
X.509 certificate (Arm Chain of Trust). 参考:ARM X.509 certificate
Note,当前芯片是LS1406,不支持ARM的x.509版本的验证,因此以CSF headers (NXP Chain of Trust)为主。
对于基于TF-A的secure boot流程简述如下:
SoC从reset状态释放之后,控制权hands off BL1。BL1的主要负责去验证BL2的image和BL1自己image header中的信息是否匹配。接着,BL1读取
BOOTLOC指针的值(这个值在BL2 image header中)。BL2如果被验证成功。BL2 image进一步验证FIP image的每一个header。FIP image主要包含:
X.509 certificate/CSF header BL31 + BL31 image
X.509 certificate/CSF header BL32 + BL32 image (optional)
X.509 certificate/CSF header BL33 + BL33 image
BL33(uboot)负责验证和执行uboot所引导层级的固件。
TF-A引导secure boot流程:

1.2 secure images format
1.2.1 bl2_<boot_mode>.pbl
在pbl文件中,主要包含RCW和bl2.bin文件。NXP为bl2.bin文件创造了CSF头文件。

1.2.2 fip.bin
在fip.bin文件中,包含BL31,BL32(optee.bin),BL33(uboot/uefi),每一个固件都有一个文件头。

2. Secure Boot High-Level
2.1 签名和验签
2.1.1 code sign tool签名

这部分由Code Signing Tool (CST)完成。需要输入:
私钥和公钥
image
CSF header (Command Sequence File header)
S/G Table (Scatter Gather table)
会输出:
signature
public key hash (放入eFUSE)
2.1.2 验签过程

验签过程由设备端处理器完成。
2.1.3 签名验签元素说明
CSF header
Command Sequence File header,主要提供一些image验证信息,例如flag,image指针,offset和长度等。有两个版本分别应用于不同的TA版本(ISBC and ESBC),后面会讲。LS1046A支持是TA2.X版本。
SG table
Scatter Gather table,可选的。使用该table允许使用不连续的images。
Public key list
Super Root Key (SRK) table(后面会展开讲)。一个或多个公钥被放在image后面。然后有CSF头来指定签名验证。
signature
最后的签名是,CSF header + SG Table + image + Public key list的集合的SHA256值,被RSA私钥进行签名。
2.2 信任链
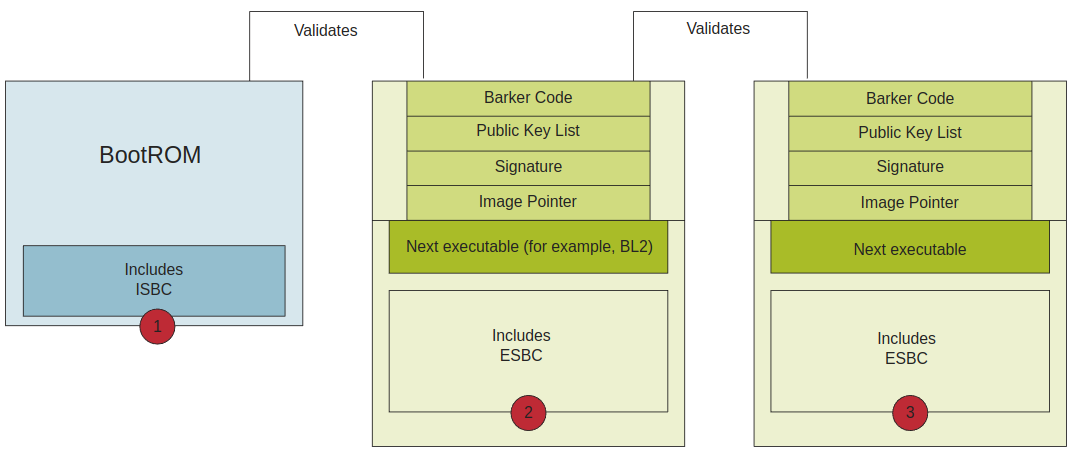
Chain of Trust (CoT)确保只有被认证的image能够被执行在特定的平台。image在CoT认证可以被分为两个阶段:
Pre-boot and ISBC (详见2.2.1)
ESBC (详见2.2.2)
为了保证image的加密特性,image可以被加密以blobs的形式存储在flash中。ESBC uboot image程序可以使用Cryptographic blob mechanism来创建保密特性的信任链。QorIQ Trust Architecture 3.0 User Guide
2.2.1 pre-boot & ISBC (BootROM)
ISBC(Internal Secure Boot Code)是嵌入存储在SoC的BootROM中的验证程序。根凭证的验证程序已经存储在BootROM中。ISBC需要验证下一个阶段的引导程序(在NXP的设计,这个引导程序应该是pbl文件中的BL2)。
2.2.2 ESBC (Bootloaders)
External Secure Boot Code (ESBC),BL2有数字签名验证程序(ESBC)嵌入其中,BL2在执行它之前会进行验证。
ESBC是NXP提供的secure boot的参考实现,用于验证在TFA中的image和uboot image。uboot用于验证Linux,设备树之类的。
NXP提供了相同的ESBC,但是对于ISBC,不同平台有不同的程序。这些平台根据不同的Trust Architecture(TA)种类不同,提出两种:
TA 2.x or hardware pre-boot loader (PBL) based platforms
TA 3.x or Service Processor (SP) based platforms
NXP-LS1046A属于TA2.x平台。
3. Secure Boot Low-Level
Secure boot low-level主要涉及:
BootROM阶段
Bootloaders阶段。
3.1 Pre-Boot phase (BootROM)
BootROM阶段的程序是有没有办法修改。这里只能明白其工作和原理。NXP的LS1046A芯片使用的TA 2.x 平台的 bootrom程序。
在开发调试阶段,设定RCW[SB_EN] = 1来设定系统启动以secure boot的形式启动。在量产阶段,设定ITS bit in SFP确保系统执行在secure模式。一旦SFP ITS被写入到FUSE当中,就不能改变了。
Hardware pre-boot loader
PBI程序( pre-boot initialization commands),一旦启动secure boot,其必然被PBL执行。在PBI命令中必须包含加载ESBC的指向CSF header的指针数据(SCRATCHRW1寄存器中)。
接着BootROM程序(ISBC)读取寄存器来判断CSH Header指定的下一个image在哪里,准备进入到验证阶段。如果启动备选image,第二条加载备选image的CSF header的PBI命令会被加载到SCRATCHRW3寄存器。
在LSDK参考实现中,boot源不受到影响,PBI命令被置入到RCW中来加载BL2的image到OCRAM上。在启动secboot的情况下,验证BL2的CSF header也会随着使用PBI命令的BL2一起被加载到OCRAM上。
(这部分知道做什么就可以,无法修改,并不是重点)
ISBC phase
当SoC上电之后Power-on Reset (POR),主CPU0被释放,开始执行BootROM上的程序。
过程如下所示:
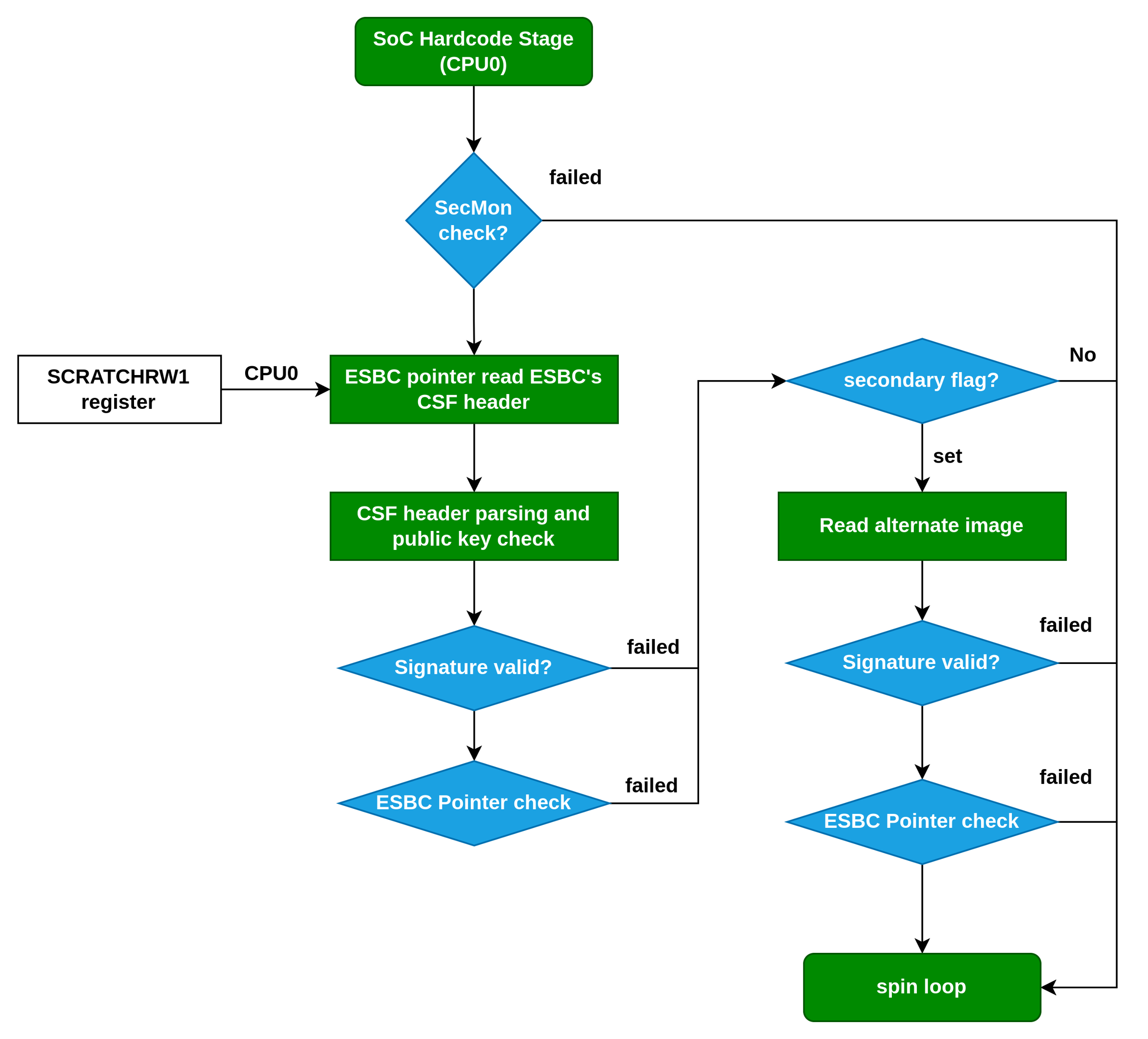
SecMon check :CPU0需要确认SecMon的状态,如果SecMon状态没有就绪则进入spinloop状态。
ESBC pointer read:CPU0从SCRTCHRW1寄存器读取ESBC的CSF header的地址,然后从地址拿到文件头信息。此过程会判断header中的barker-code以此判断是否符合平台。
CSF header parsing and public key check:如果CPU0找到了一个正确的CSF头文件,从CSF头中解析public key。在header中可能存在一个或者一组public key。SFP寄存器不会真正存储public key,它只是存储它的sha256的hash值。如果算出的pubhash和存储在SFP中的不相同的话,那么失败。
Signature validation:如果是一个正确的pub hash值,那么就开始对header + image + public keys 一起做RSA验签操作。
ESBC Pointer check: CSF header包含 入口地址。会检测地址范围是否正确。然后,call sec mon进入安全模式,并跳转到入口地址。
如果失败的话,会进入到备选模式,ISBC会从SCRATCHRW3寄存器读取备选image的文件头信息,然后再进入验证。如果备选模式失败,那么就进入到spin loop状态了。
ISBC header
ISBC的header和ESBC的header如图所示:

详细参考: https://docs.nxp.com/bundle/GUID-487B2E69-BB19-42CB-AC38-7EF18C0FE3AE/page/GUID-4D5D0916-29CC-4E11-BF82-477C40F31585.html
Super Root Keys (SRKs) and signing keys
RSA的密钥对中其中私钥用于签images,公钥用于验证image。公钥被嵌入到了embedded image中,并且被计算hash值存储到了eFUSE上。secboot支持key的长度是1k/2k/4k。
需要注意的的是,rsa私钥需要保护好,如果私钥暴露,攻击者完全可以使用rsa产生一个备选的image存入SCRATCHRW3来pass secure boot。
3.2 ESBC phase (Bootloaders)
不像是BootROM阶段的,ESBC阶段的code可以被我们修改。Nxp定义的ESBC包含:
BL2 image(验证BL31/BL32/BL33 image)
uboot image (验证linux / dtb)
ESBC的程序在LSDK中已经提供。NXP提供两个类型的secure boot:
ESBC image validation using NXP CSF headers
also known as NXP CoT for ESBC images
ESBC image validation using X509 certificates
Enabled on NXP platform through TF-A
meets Arm recommended Trusted Board Boot Requirements (TBBR)
also known as Arm CoT for ESBC images
需要注意的是,Arm CoT is supported only for LX2160ARDB and LX2162AQDS platforms. 因此,NXP-LX1046A不支持ARM的。
BL2 binary将会加载以下binaries:
BL31 binary
BL32 binary (OPTEE code)
BL33 binary (U-Boot/UEFI)
这部分验证过程和ISBC phase是一致的。
4. Code Signing Tool
code sign tool主要就是生成符合NXP验证的secure boot的文件头。内部的实现是通过调用OpenSSL APIs。
主要功能如下:

4.1 key gen
genkey
RSA的key pair从以下3部分来:N, E, D:
N – Modulus
E – Encryption exponent
D – Decryption exponent
Public key: 来源于E&N Private key: 来源于D&N
生成key需要注意:
支持三种长度的key 1024 / 2048 /4096;
生成的key格式是pem格式;
可以自定义名字。
gen_otpmk_drbg
工具可以插入hamming code在用户定义的256b的十六进制字符串中。也可以产生256b的随机数并插入hamming code。这个需求可以通过gen_otpmk_drbg完成。
./gen_otpmk_drbg --b <bit_order> [--s <string>] [--u]
生成drbg随机数:
./gen_drv_drbg <hamming_algo> [string]
4.2 header creation
uni_pbi
参考: https://docs.nxp.com/bundle/GUID-3FFCCD77-5220-414D-8664-09E6FB1B02C6/page/GUID-E0B02E68-62BC-4043-ABF3-95804A92D85A.html
uni_sign
uni_sign tool能够被使用如下:
CSF header generation along with signature for both ISBC and ESBC phases
CSF header generation without signature if private key is not provided
uni_sign tool (with ESBC = 0 in input file) is used for creating signature and header over Boot1 image to be verified by ISBC
uni_sign tool (with ESBC = 1 in input file) is used for creating signature and header over images to be verified by ESBC
运行命令:
参考: https://docs.nxp.com/bundle/GUID-3FFCCD77-5220-414D-8664-09E6FB1B02C6/page/GUID-054242AF-D433-427B-B020-2602CAA777E7.html
4.3 signature gen
gen_sign
这个工具还能提供计算signature的功能。只需要hash file和私钥作为输入。
./gen_sign [option] <HASH_FILE> <PRIV_KEY_FILE>
参考: https://docs.nxp.com/bundle/GUID-3FFCCD77-5220-414D-8664-09E6FB1B02C6/page/GUID-A07DA501-2E7C-41FC-B635-3AD1F917A5D0.html
sign_embed
把sign的结果嵌入到header里面则需要使用这个工具。
./sign_embed <hdr_file> <sign_file>
参考: https://docs.nxp.com/bundle/GUID-3FFCCD77-5220-414D-8664-09E6FB1B02C6/page/GUID-8BEAD88D-4D01-4632-9C1F-7E72805D2B3E.html
5. Secure Boot Enabling
Secboot流程能允许被执行:
Chain of Trust (不加密,仅开启签名验签)
Chain of Trust with confidentiality (加密和签名验签)
5.1 secure boot exec flow
总体流程如图所示:
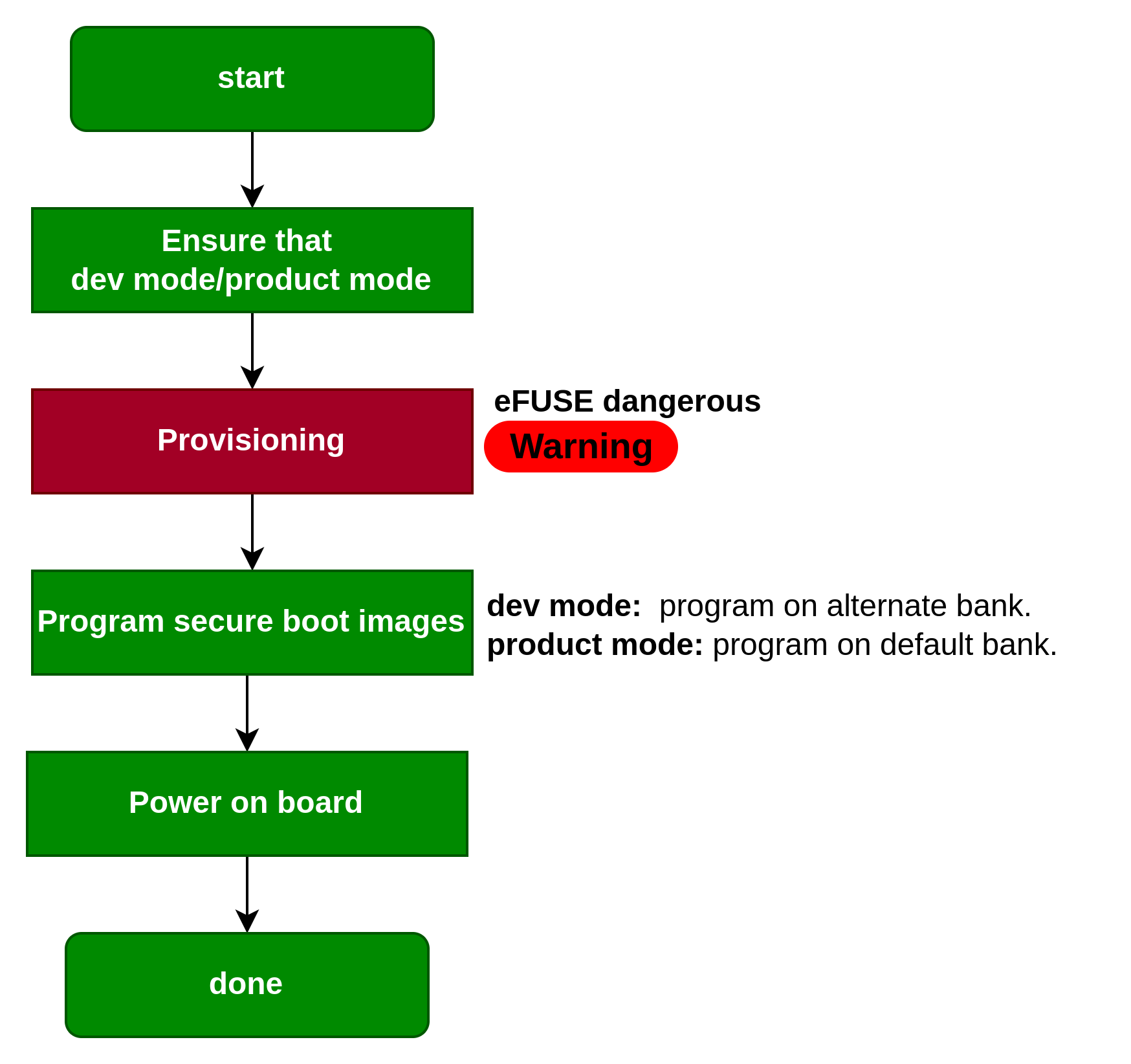
开发模式确认
我们需要确定是开发模式还是产品模式。如果是开发模式,不要进行ITS fuse的熔断,设定RCW[SB_EN] = 1就可以开启secure boot;如果是开发模式,则需要熔断ITS在SFP。
Provisioning
无论是开发模式还是在产品模式,都有熔断eFUSE的需求,OTPMK and SRKH两个位需要注意。OTPMK 需要使用gen_otpmk_drbg产生符合质量的随机数。详见Provisioning。熔断OTPMK是必须的,无论是产品模式还是开发模式。
Program secure boot images
在产品模式,只需要把secure boot images烧写到默认bank地址即可。在开发模式,需要编写到alternate bank 地址,由default bank切换到alternate bank再去启动secure boot。
power on board
无image加密
在没有image加密的情况下:
如果secure boot 烧写到默认bank(both dev and product mode),ISBC code获取控制权,并且验证ESBC的image。ESBC进一步验证linux/rootfs/dtb的signature。
如果secure boot烧写到 alternate bank中(dev mode),板子启动将会从默认的bank启动。当切换到alternate bank的时候,ISBC code获取控制权,并且验证ESBC的image。ESBC进一步验证linux/rootfs/dtb的signature。最后启动linux。
image加密
如果image使能了加密:
如果secure boot 烧写到默认bank(both dev and product mode),ISBC code获取控制权,并且验证ESBC的image。ESBC进一步验证linux/rootfs/dtb的signature。
First boot:封装步骤(应在OEM工厂内进行)
默认情况下,encap和decap引导脚本将安装在引导分区中。
在生成所有映像后,当板首次启动时,encap bootscript将执行。此引导脚本:
验证和封装Linux和dtb映像,并用新封装的Linux和dtb替换未加密的Linux和dtb映像。

将encap引导脚本和头替换为已存在于引导分区中的decap引导脚本及其头。
emit reset信号。
Subsequent boot:
如果安全引导映像在默认库中闪存(用于生产/开发阶段):
U-Boot将使用decap命令执行脚本
在DDR中Un-blobify linux和dtb映像。
将控制权传递给这些images。

如果secure boot烧写到 alternate bank中(dev mode),板子启动将会从默认的bank启动。当切换到alternate bank的时候,ISBC code获取控制权,并且验证ESBC的image。ESBC进一步验证linux/rootfs/dtb的signature。最后启动linux。
5.2 prepare board for secure boot
enable POVDD
检查POVDD引脚,对于LS1046RDB,需要Put J21 to enable PWR_PROG_SFP。参考LS1046A的datasheet。
该引脚为SFP,引脚如图:

需要在硬件设计上引出该引脚,为Provisioning做准备。

Byte swap for reading and writing SRKH/OTPMK
应谨慎编写SRKH和OTPMK。如果使用Core写入SRKH和OTPMK,则需要交换SRKH与OTPMK。但是,如果使用DAP或SFP写入SRKH和OTPMK,则不需要交换。有关详细信息,请参阅下表。

参考: https://docs.nxp.com/bundle/GUID-3FFCCD77-5220-414D-8664-09E6FB1B02C6/page/GUID-036CF49E-4211-48B8-803A-870C57777C8A.html
Program OTPMK
After enabling POVDD, follow these steps to program OTPMK at U-Boot:
参考: https://docs.nxp.com/bundle/GUID-3FFCCD77-5220-414D-8664-09E6FB1B02C6/page/GUID-F780D1D5-F1B2-478B-86AE-267D74F9C790.html
Program SRKH mirror registers
参考: https://docs.nxp.com/bundle/GUID-3FFCCD77-5220-414D-8664-09E6FB1B02C6/page/GUID-2CF1D60F-C79F-4A35-800B-2BFE504EBAC5.html
Write SFP_INGR register
参考: https://docs.nxp.com/bundle/GUID-3FFCCD77-5220-414D-8664-09E6FB1B02C6/page/GUID-EFF8FF41-C8C0-4A3B-AF95-E801D585B7C6.html
5.3 build secure boot image
5.3.1 using flexbuild
After setting up the flexbuild environment, run the following commands to generate images for NXP CoT:
For example:
The images will be available at: /build/images/.
5.3.2 using manually TF-A
需要在TF-A中设定:
Set
TRUSTED_BOARD_BOOT=1to enable trusted board boot. NXP CoT is enabled automatically whenTRUSTED_BOARD_BOOT=1andMBEDTLS_DIR pathis not specified.
Specify path of the CST repository as
CST_DIRto generate CSF headers. In NXP CoT, CSF header is embedded to the BL31, BL32, and BL33 images.Default input files for CSF header generation are available in
CST_DIR.As per the default input file, you need to generate following RSA key pairs and add them to the ATF repository:
srk.pri
srk.pub
The RSA key pairs can be generated using the gen_keys CST tool. To change the input file, you can use the options
BL33_INPUT_FILE,BL32_INPUT_FILE,BL31_INPUT_FILE.
注意:TRUSTED_BOARD_BOOT 也可以被使能在非安全启动。 然而,ROTPK在非安全启动流中被忽略,并且故障不会导致SNVS转换。
To prepend CSF headers to BL31, BL32, and BL33 images:
The secure boot binaries for NXP CoT are available in the atf directory:
build/<platform>/release/fip.binbuild/<platform>/release/bl2_flexspi_nor_sec.pbl
6. Provisioning
NXP的Trust Architecture (TA),提供片上FuSE(OTP)。通过Security Fuse Processor (SFP)来配置以下寄存器:
One Time Programmable Master Key Registers (OTPMKRs)
Super Root Key Hash Registers (SRKHRs)
Debug Challenge and Response Value Registers (DCVRs and DRVRs)
OEM Security Policy Registers (OSPRs)
OEM Unique ID/Scratch Pad Registers (OUIDRs)
6.1 FuSe Programming Scenarios

6.2 Fuse Provisioning during OEM Manufacturing
这一步被分为两个阶段:
Stage 1: (Non-secure boot) – Minimal Fuse Provisioning
Stage 2: (Secure Boot) – Final Fuse Provisioning
stage 1
如果启动secureboot 最小的配置项需要兼顾如下:
SRKH
CSFF
Minimal OTPMK
此阶段不通过安全引导来执行,但必须设置FuSe,以便下一次引导通过安全引导。如果这一步骤发生在可信的环境中,OEM可以选择在这一阶段自行编写所有保险丝。
stage 2
剩下的FuSe可以在secure boot启动的时候进行编写。注意,此步骤导致OEM阶段FuSe熔断,FuSe不再可写。
6.3 Fuse Provisioning Utility
NXP的安全固件中包含了做Provisioning的固件,这个固件编译可以参考下面 build fuse provisioning firmware image一节。
关于fuses值的信息将通过fuses文件提供。fuses文件是一个二进制文件,具有指示fuses及其相应值的位。CST提供了一个输入文件,用户可以在其中输入所需的值。该工具生成一个fuses文件,该文件在BL2映像中解析以进行fuses配置。安全固件将进行必要的检查,以确定所提供的输入值是否正确。例如,当SFP保险丝中已设置OEM_WP时,无法对OTPMK、SRKH进行编程。
fuse file structure
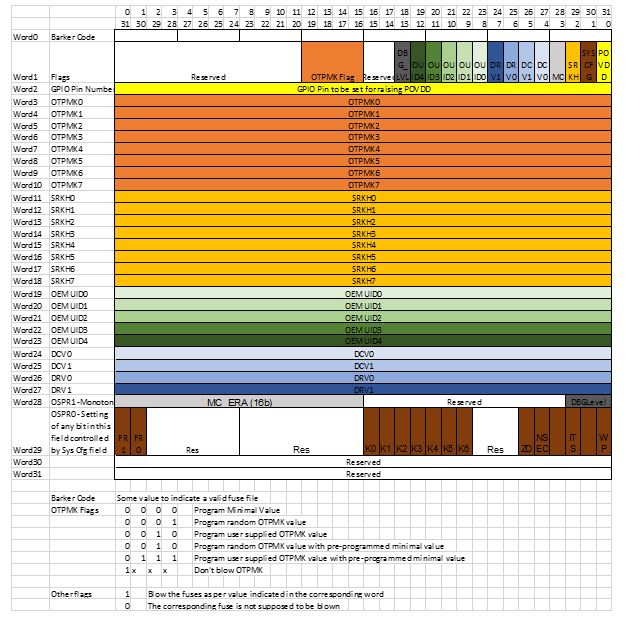
配置文件示例
6.4 Deploy and run fuse provisioning
分为以下步骤:
开启POVDD
编译Provisioning firmware image
部署image到板子上
执行Provisioning
开启POVDD
检查PWR_PROG_SFP引脚,高电平有效。
编译Provisioning firmware image
编译CST
$ flex-builder -c cst编译Provisioning firmware(在编译firmware之前需要配置):
Set
CONFIG_FUSE_PROVISIONING=yin fileflexbuild_<version>/configs/sdk.yml
[可选] 编辑用于Provisioning的输入文件:
The input file is available at:
<flexbuild_dir>/components/apps/security/cst/input_files/gen_fusescr/<device>/input_fuse_file,注意<device>可以是ls2088_1088orls104x_1012
生成image:
<machine>can be ls1012ardb, ls1012afrwy, ls1021atwr, ls1028ardb, ls1043ardb, ls1046ardb, ls1046afrwy, ls1088ardb_pb, ls2088ardb, lx2162aqds<boottype>can be nor, sd, emmc, qspi, xspi, nand
最后生成新的img位于:
flexbuild_<version>/build/images/firmware_<machine>_<boottype>boot.img
Deploy and run fuse provisioning firmware image on board
通过uboot烧写 firmware_ls1046ardb_sdboot.img ,可以把 firmware_ls1046ardb_sdboot.img 放在sd卡中,使用uboot来把这个img烧写到mmc中。
也可以通过手动烧写 https://docs.nxp.com/bundle/GUID-487B2E69-BB19-42CB-AC38-7EF18C0FE3AE/page/GUID-87C3A500-F0D7-4DD9-B5F1-112C58EE54E4.html
Validate fuse provisioning
启动uboot之后,进入uboot操作界面。检查DCFG scratch 4寄存器是否存在错误代码。例如,对LS1046ARDB运行以下命令以检查错误代码:
如果md命令未显示任何错误,则Provisioning成功。
Error code可以参考: https://docs.nxp.com/bundle/GUID-487B2E69-BB19-42CB-AC38-7EF18C0FE3AE/page/GUID-BC1D24DA-1DE4-4155-9F6C-F1E69315545E.html
7. U-Boot Secure feature
7.1 一些在uboot环境中的命令
为了建立安全启动信任链,一些 U-Boot 命令已添加到 ESBC 代码中。
esbc_validate command
验证CSF header的命令。
esbc_validate <img_hdr> [<pub_key_hash>]
img_hdr
image的CSF header位置
pub_key_hash
用于验证image的公钥hash。可选,如果不提供则使用ISBC一样的key
esbc_halt command
可以让处理器进入spin loop状态。
blob enc command
此命令将创建放置在 src 位置的image加密成blob形式,并将该 blob 放置在 dst 位置。
src location
需要加密的image地址
dst location
blob输出的地址
length
需要加密的image的长度
key_modifier address
放置一个 16 字节长的随机数(key modifier)的地址
blob dec command
此命令将解密放置在 src 位置的 blob的解密结果放置在 dst 位置。
src location
需要解密的blob地址
dst location
解密后的image输出的地址
length
需要解密的image的长度
key_modifier address
放置一个 16 字节长的随机数(key modifier)的地址
7.2 Bootscript
Bootscript是uboot image的一个执行脚本,内部包含了执行uboot的命令。ESBC在除了验证uboot之外,还会在验证执行uboot之前验证bootscript。bootscript有一些规则需要遵守:
Bootscript 可以包含 U-Boot 支持的任何命令。而secure boot不对脚本内调用的命令是否正确进行验证,换句话说,secure boot假设script上所有的命令都是正确的。
如果bootscript中出现了一些语法错误,会导致boot进入spin loop状态;
在uboot脚本中使用验证命令,不支持分散的images;
如果ITS fuse被熔断,任何在验证image的时候的错误都会导致系统reset。因此查找错误应该在这次启动之前的log中寻找 。
ESBC的U-Boot 期望从flash加载引导脚本。 ESBC的U-Boot 代码假定用于签署引导脚本的公钥/私钥对与签署 U-Boot 映像时使用的公钥/私钥对相同。 如果用户使用不同的密钥对对镜像进行签名,则密钥对的 N 和 E 分量的哈希应在宏中定义:
7.2.1 Chain of Trust
Bootscript 包含有关下一级image的信息,例如 MC,Linux ESBC 根据它们的公钥验证这些image。 如果需要,MC 使用经过验证的 MC 映像启动,最后执行 bootm 命令以将控制权传递给 Linux 映像。

上面图片的bootscript示例:
7.2.2 Chain of Trust with confidentiality
为了建立具有机密性的信任链,可以使用加密的 blob 机制。 在这个信任链中,经过验证的image被允许使用一次性可编程主密钥(One Time Programmable Master Key)来解密系统image信息。 将使用两个引导脚本。 首先使用封装引导脚本创建下一级image(例如 MC、Linux)的 blob 并将它们保存在闪存上。 在此之后,在将封装引导脚本替换为解封装引导脚本后启动系统,解封装 blob 并启动 MC 和 Linux。
加密

解密

8. Secure Boot Overview
This section describes the steps to run secure boot on NXP Layerscape family SOC-based boards:

The procedure to run the secure boot is shown in the following steps:
Prepare board for secure boot
Build secure boot images for NXP CoT and Arm CoT
Note, Red blocks are dangerous, and can't take it back.
9. Enabling Secure Boot
9.1 Enable POVDD
The use of the trust architecture feature is dependent on programming fuses in the Security Fuse Processor (SFP). To program SFP fuses, the user is required to supply 1.8 V to the TA_PROG_SFP pin Power sequencing. TA_PROG_SFP should only be powered for the duration of the fuse programming cycle, with a per-device limit of six fuse programming cycles. At all other times, TA_PROG_SFP should be connected to GND. The TA_PROG_SFP pin is shown in the following figure:

This figure shows the TA_PROG_SFP timing diagram:

9.2 RCW modifying
The reset configuration word (RCW) resides in non-volatile memories (for example, NOR, QSPI, SDHC). It gives the flexibility to accommodate a large number of configuration parameters to support a high degree of configurability of the SoC. Configuration parameters generally include:
Frequencies of various blocks including cores/DDR/interconnect.
IP pin-muxing configurations
Other SoC configurations
The RCW's provided with the release enable the following features:
Boot location as NOR flash
Enables 4 UART without flow control
Enables I2C1, I2C2, I2C3, I2C4, SDHC, IFC, PCIe, SATA
How to change RCW?
RCW[SB_EN] = 1 can be set by the following figure:

Build the new RCW file:
$ flex-builder -i clean-firmware
$ flex-builder -c firmware -a arm64 -m ls1046ardb -b sd -S 1040

Cat RCW file

In the LS1046A Reference Manual - 4.4.6.1 RCW Field Definitions, the offset of the SB_EN is 202 (0xCA) bits.

The position of the SB_EN is fixed in the following figure:

9.3 Blown eFUSE
9.3.1 Provisioning Ordering
SRKH and OTPMK should be carefully written keeping in mind the SFP Block Endianness. If SRKH and OTPMK are written using Core, SRKH and OTPMK need to be swapped. However, if SRKH and OTPMK are written using DAP or SFP, swap is not required. Refer the following table for details.
Console
SRKH/OTPMK generated order from CST
SRKH/OTPMK write order
SRKH/OTPMK Read order
Endianness
U-Boot
order_1
reverse order_1
reverse order_1
Core endianness
CCS
order_1
order_1
order_1
SFP endianness (DAP)
Assuming following SRKH values are generated:
Execute the following commands at the CCS console to permanently write SRKH using DAP/SFP:
Execute the following commands at the U-Boot console to permanently write SRKH using core:
9.3.2 Program OTPMK
After enabling POVDD, follow these steps to program OTPMK at U-Boot:
Verify
Verify the SNVS register - HPSR to check whether OTPMK is fused already.
OTPMK_ZERO_BIT (second nibble) is 1, indicating that OTPMK is not fused. The second nibble of 88000900 is 1 indicatesthe OTPMK is not fused.
Gen OTPMK
Generate OTPMK by CST ./gen_otpmk_drbg -b 2

Fuse OTPMK
Note, write order !!!
Check OTPMK
At the U-Boot prompt, verify that the SNVS registers for OTPMK are correctly written.
Check if OPTMK is fused.
OTPMK_ZERO_BIT (second nibble) is 0, indicating that OTPMK is fused.
Read OTPMK:
Note: OTPMK is not visible in plain.
9.3.3 Program SRKH mirror registers
After enabling POVDD, follow these steps to program SRKH registers at U-Boot:
verify
Check if SRKH is fused.
Zero indicates that SRKH is not fused.
Fuse SRKH
The CST tool will generate the SRK by inputting public key.

SRKH should be carefully written considering the SFP block endianness.
Check
Then, the following could be the value of dumping SRKH.
=> md $SRKHR0 0x10
SRKH is visible in plain because of the SFP block endianness.
2.3.3 Program SFP_INGR register to LOCK FUSE
CAUTION: Do not proceed to the steps in this topic, until you are sure that OTPMK and SRKH are correctly fused, as explained in the topics above. After the next step, fuses are burnt permanently, which cannot be undone.
Write SFP_INGR[INST] with the PROGFB(0x2) instruction to blow the fuses.
=> mw $SFP_INGR_REG $SFP_WRITE_DATA_FRM_MIRROR_REG_TO_FUSEReset the board.
9.4 Image Signing
According to the NXP CST tool, the RSA (PKCS#1 format) is supported by CST. Please refer to the link [LS104x] secure boot
One image signing process is shown in the following figure:

9.4.1 uni_sign
uni_sign tool can be used for the mode that the CSF header generation without signature if a private key is not provided.
According to the uni_sign, you should assign a “NULL” value to the PRI_KEY field (following figure)

Meanwhile, use the --img_hash argument when executing the uni_sign tool. (following figure)

The image’s hash.out in a binary file, the public key's SRK hash in the console, and the CSF header in a binary file are outputted by the uni_sign after ./uni_sign --img_hash input_ppa_secure executed.
9.4.2 Sign Server signing the hash
The image’s hash.out in a binary file shall be signed by the signing server or the HSM so that the private key cannot be exported. The HSM signing process should aligned with the C programming:
The API RSA_Sign in the OpenSSL is invoked by the signing process. https://www.openssl.org/docs/man3.0/man3/RSA_sign.html.
Please distinguish between digest-RSA signing and RSA signing. The RSA_sign only use the RSA algo to sign the data and did not calculate the input data hash value, even if you specified the hash type NID_sha256.
I have developed a tool to verity the HSM signed image using the public key, https://github.com/carloscn/script/tree/master/c_opssl_verify
./verify_tool pskv1.pem sign.out.1 hash.out

Note, you should assign the PKCS#1 format key. The OpenSSL generated key is PKCS#8 format by default.
9.5 image encryption

10. Testing
Terms and Abbreviations
CST
制作secureboot image的工具,参考:Code Signing Tool
OTPMK
fuse上的一个位域,参考:Program OTPMK
SRKH
fuse上的一个位域,参考:Program SRKH mirror registers
SFP
SFP_INGR寄存器,用于配置FuSe,参考:Write SFP_INGR register
OEM_WP
OEM阶段fuse上的一个位域,参考:Fuse Programming Scenarios
CSFF
OEM阶段fuse上的一个位域,参考:Fuse Programming Scenarios
OEM
原始设备制造商简称_OEM_,OEM是英文Original Equipment Manufacturer的缩
POVDD
芯片上的一个引脚引脚 Enable POVDD
CSF
NXP Chain of Trust image header 参考: secure boot - Introduction
ISBC
Internal Secure Boot Code,例如bootrom boot code
ESBC
External Secure Boot Code,例如uboot
ITS
FuSe上的一位,烧写该位代表secure boot使能于产品模式,而不是调试模式。参考: Secure boot execution flow for Chain of Trust
MC
Management Complex firmware, 用于管理内存,LS1046A没有这个固件。 参考: Management Complex: How DPAA2 objects are created and managed
---
---
最后更新于